Ransomware is one of the greatest cyber security threats that organisations currently face. In recent years, it has been growing in size, scale and sophistication.
Last year alone, 73% of companies were hit with a ransomware attack, and by the end of the year, it is expected to cost the world more than £8 billion in damages.
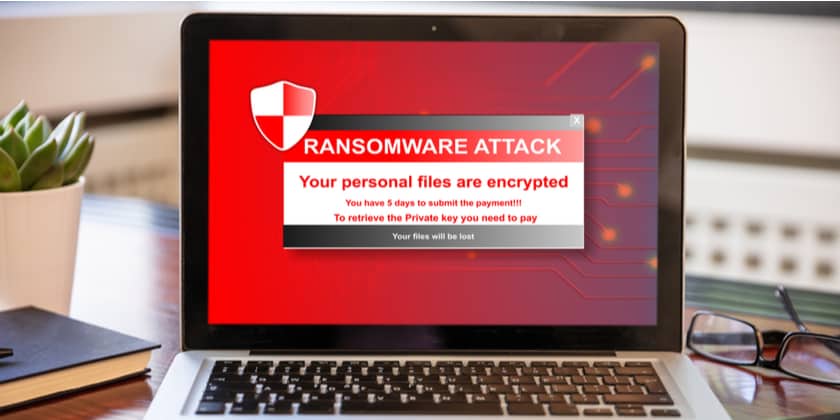
Ransomware is a type of malware that prevents users from accessing their system by encrypting files and demanding a ransom payment for the system to be unlocked. The ransom payment is usually requested in Bitcoin or in other cryptocurrencies that are difficult to trace. Cybercriminals will typically assign a deadline for the ransom to be paid, and if the deadline passes, the ransom payment will be doubled or the files permanently locked.
Certain variants of ransomware are designed to spread rapidly to other machines on a network. This is exactly what happened in the 2017 WannaCry attack when the ransomware encrypted hundreds of thousands of computers in more than 150 countries. Within a matter of hours, the ransomware wreaked havoc across the world, bringing a third of the UK’s NHS trusts to a virtual standstill.
How to Prevent Ransomware
There are several different ways that ransomware can infect a device. One of the most popular ways to attack organisations is through the use of malicious emails. The email will appear entirely legitimate and contain a link or attachment that once opened will deliver ransomware on to the system.
MetaPhish, our phishing simultation software, provides customers with a powerful defence against ransomware attacks attacks by training employees how to identify and respond appropriately to these threats. The software contains a library of smart learning experiences such as infographics, notices, and training videos and unlike other phishing solutions, the software allows the user to communicate back to the administrator.
MetaPhish enables organisations to find out just how susceptible their company is to fraudulent phishing emails and helps identify those users that require additional training.



